Detailed presentation by themes
(1) Chaotic light emission in a semiconductor laser with optical feedback
Reflecting part of the laser’s own emitted beam back to its cavity as a feedback beam is a typical method to generate chaos. Semiconductor lasers are commonly used in CD players and optical communication systems. It may happen that the surface of a disk or an optical fibre connector act as reflectors, sending back to the laser part of its emitted light and causing it thus to generate irregular and chaotic output signals.
Figure 1(a) schematically presents a semiconductor laser with optical feedback. The laser beam is reflected by an external mirror and fed back to the laser’s internal oscillating cavity. Under the action of this feedback beam, nonlinear interactions between the photons and the carriers present in the active region of the laser occur, resulting in instabilities of the optical power in the internal cavity. In consequence, the optical signal emitted by the laser can show chaotic evolutions as illustrated in Figure 1(b). Fast oscillations with frequencies reaching the GHz order (period of the nanosecond (10-9 s) scale) can be observed. This frequency range corresponds to the relaxation oscillation frequency of the laser.
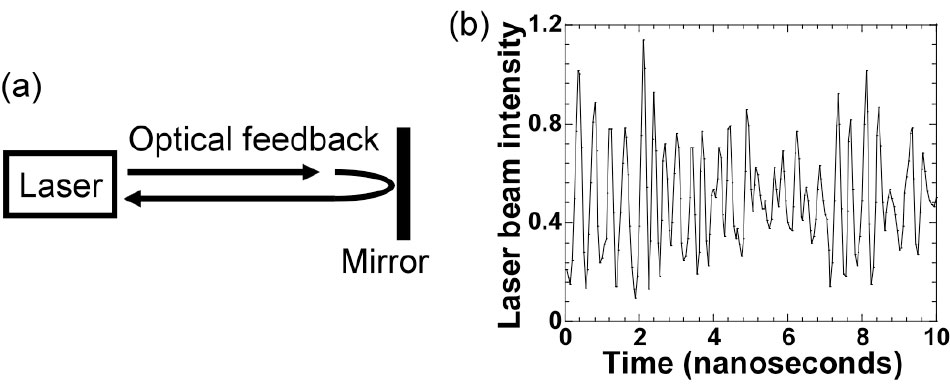 Figure 1: Schematic set-up (a) of a laser with optical feedback and chaotic output waveform obtained (b).
Figure 1: Schematic set-up (a) of a laser with optical feedback and chaotic output waveform obtained (b).
Although chaotic laser outputs have been observed in various laser systems, very few research fields actually focus on such instabilities. In many applications, techniques to prevent irregularities in lasers are commonly being used. In most engineering applications, lasers emitting stable single-mode (only one wavelength) beams and the use of methods to obtain narrow spectral bandwidth are recommended. In order to yield stable laser output beams, it is necessary to remove all instabilities from them.
From the point of view of research in nonlinear dynamics, the instabilities seen in laser beams are high-valued experimental manifestations of the nonlinear dynamics theory. Moreover, by actively combining laser and chaos, novel engineering applications such as optical secret communication or fast random number generation have emerged.
