Research themes in the Uchida Lab
(4) Reinforcement learning using chaotic semiconductor laser
1.Multi-armed bandit problem
The multi-armed bandit problem is a problem using reinforcement learning, where a player repeatedly selects one of multiple slot machines with unknown hit probabilities to maximize the total reward [1]. This problem can be used for applications in stock trading [2] and efficient wireless communications [3]. The procedures for solving this problem are known as “exploration” and “exploitation.” Exploration is a procedure of selecting one of multiple slot machines to estimate their hit probabilities. Exploitation is a procedure of selecting the best slot machine with the highest hit probability to maximize the total reward. However, exploration and exploitation have a difficult tradeoff, and it is known as the exploration-exploitation dilemma.
One of the algorithms for solving the multi-armed bandit problem is the tug-of-war method [4]. In this method, the probability of selecting one of two slot machines is determined by the length of the tug, and the position of the center of the tug is moved based on the result of slot machine selection, as shown in Figure 1. The probability of selecting one of the two slot machines is proportional to the length of the tug from the center.
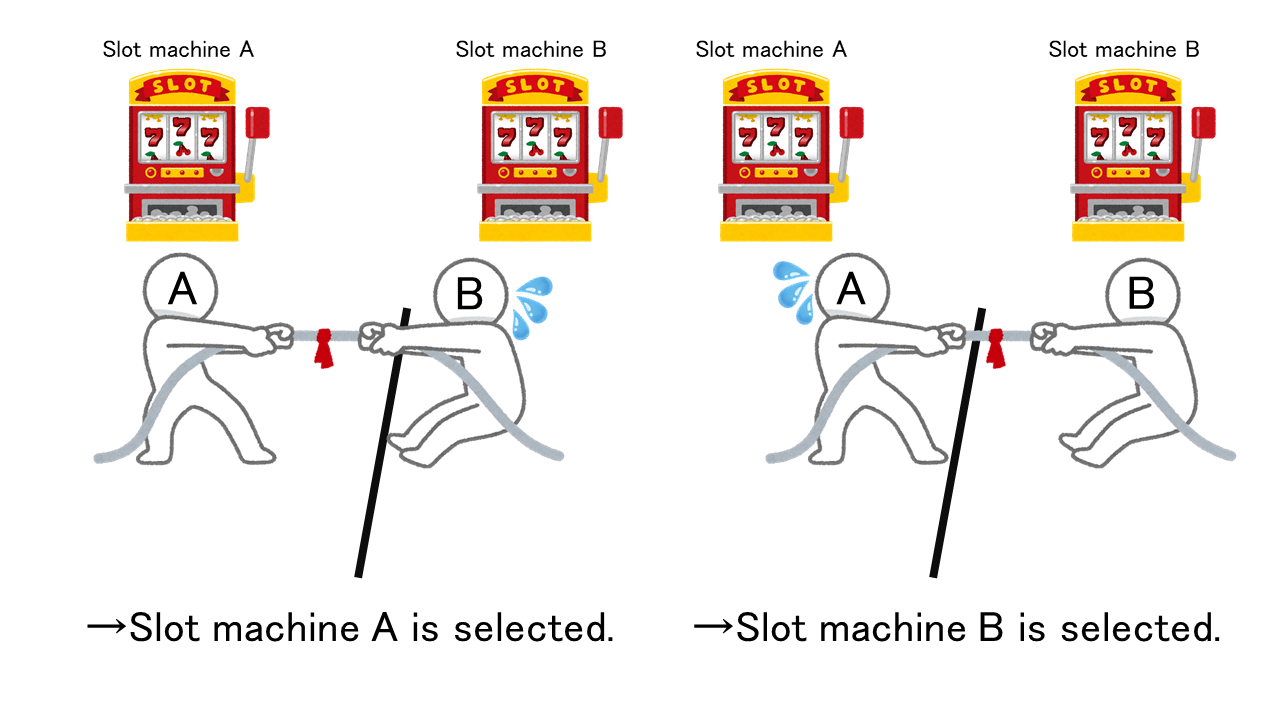 Figure 1. Schematic diagram of tug-of-war method [4].
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of tug-of-war method [4].
2.Chaotic semiconductor laser and Tug-of-war method
The tug-of-war method can be implemented using temporal waveforms of a chaotic semiconductor laser and a variable threshold [5] Figure 2 shows an implementation of the tug-of-war method using a chaotic semiconductor laser. First, chaotic temporal waveforms are sampled by an analog-to-digital converter, and the sampled value is compared with the threshold value. A player selects slot machine A if the sampled value is larger than the threshold value. On the contrary, the player selects slot machine B if the sampled value is smaller than the threshold value. Next, the threshold is changed, based on on the result of slot machine selection. For example, the threshold is decreased if the player selects slot machine A and the result is “hit.” The slot machine A tends to be more selected in the next procedure. On the contrary, the threshold is increased if the player selects slot machine A and the result is “miss.” The slot machine B tends to be more selected in the next procedure. Decision making for selecting the best slot machine can be realized by repeating these two procedures of selecting one of the slot machines and changing the threshold value.
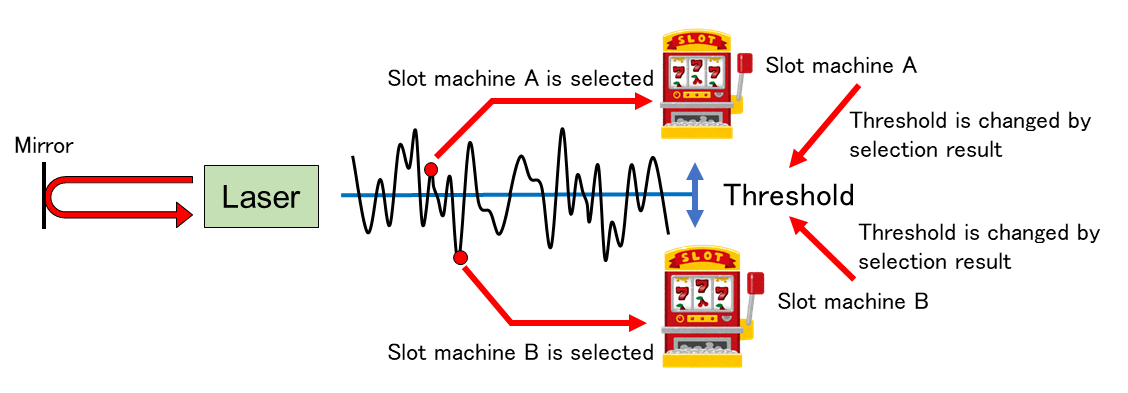 Figure 2. Implementation of tug-of-war method using chaotic semiconductor laser.
Figure 2. Implementation of tug-of-war method using chaotic semiconductor laser.
- References
- [1] H. Robbins, et al., Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 58, pp. 527 (1952).
- [2] T. Matsui, et al., EWRL2011, Vol. 7188, pp. 321-332 (2011).
- [3] L. Lai, et al., Proc. of IEEE 42th Asilomar Conference on Signals, System and Computer, pp. 98-102, 2008.
- [4] S. -J. Kim, et al., New J. Phys. Vol. 17, pp. 083023 (2015).
- [5] M. Naruse, et al., Scientific Reports, Vol. 8, pp. 8772 (2017)
