Detailed presentation by themes
(3) Consistency
Beside chaos, we have adopted in our laboratory a universal concept termed consistency as a new way of thinking [1]. Consistency is defined as the property of a nonlinear system to show reproducibility of output signals corresponding to complex signals repeatedly used as inputs to the system operating under different initial conditions. Many nonlinear systems are known to show consistency in their outputs when repeatedly driven by input signals.
A general illustration of the concept of consistency is given in figure 1. Complex signals such as deterministic chaos or random noise are used as inputs. The input signal is repeatedly injected into the nonlinear system for different arbitrary initial conditions. Each input signal generates a temporal waveform as a response from the system. These different response signals from the system are then measured, their transient parts are discarded and if the resulting output signals are identical, the system is said to achieve consistency.
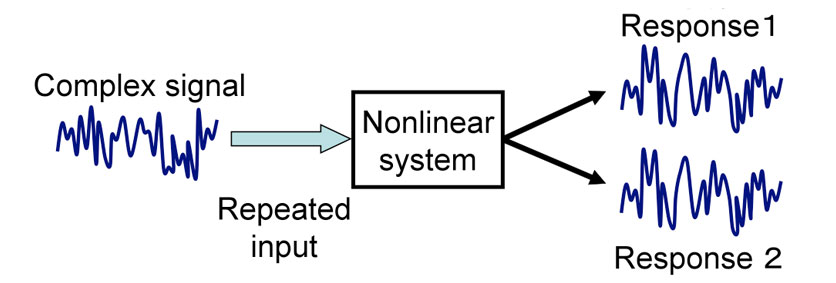 Figure 1: Consistency
Figure 1: Consistency
Consistency is a universal concept present in many natural phenomena and learning machines based on the structure of the brain. Recently, laser systems showing consistency properties have become essential elements in new optical data processing methods like reservoir computing, and are as such being subject of intense studies.
- References
- [1] A. Uchida, et al., Physical Review Letters, Vol. 93, pp. 244102 (2004).
